Over the past few years, more and more businesses have been turning to e-signatures to overcome the challenges associated with paper-based processes and boost efficiency. Besides enabling companies to get documents signed faster, electronic signatures make the signing process more convenient for everyone involved.
What are e-signatures?
An e-signature is the electronic equivalent of a handwritten signature. Individuals can use e-signatures to sign electronic documents such as employment contracts, annual reports, engagement letters, purchase and sale agreements, etc.
Creating an e-signature can be as simple as placing a text, an image, or a symbol on an electronic document with the intent to sign it.
What are the three types of electronic signatures?
Based on their level of security, the EU’s eIDAS regulation defines three types of electronic signatures:
- Simple electronic signatures (SES)
- Advanced electronic signatures (AES)
- Qualified electronic signatures (QES)
1. Simple electronic signatures (SES)
Simple electronic signatures are e-signatures that are typically created with the help of an online signature generator. Such tools allow you to either upload an image of your signature or type/draw your name on a PDF document.
Since there is no signer authentication, there is no certainty about the identity of the signer. Hence, the signer can easily repudiate the e-signature (e.g., claiming that their signature was forged, denying having signed the documents).
Therefore, in most cases, simple electronic signatures won’t hold up in court. However, it will always be up to the judge to decide, on a case-by-case basis, whether a simple electronic signature is legally binding or not.
2. Advanced electronic signatures (AES)
An advanced electronic signature is a type of electronic signature that meets the following security requirements set out by the eIDAS regulation:
- it is uniquely linked to the signer,
- it is capable of identifying the signer,
- it is created using electronic signature creation data that is under the sole control of the signer, and
- it is connected to the signed documents so that any subsequent changes can be detected.
Moreover, advanced electronic signatures must be based on one of the three ETSI standards according to the EU Commission’s Implementing Decision 2015/1506 – i.e., PAdES, XAdES, CAdES.
In Penneo Sign, you can create advanced electronic signatures using a digital ID such as MitID, BankID, itsme®, FTN etc.
Thanks to the higher level of security it provides, an advanced electronic signature can prove the authenticity of a signed document if challenged in court. However, there are a few situations where advanced electronic signatures are not enough, and the law requires a qualified electronic signature to be used instead.
3. Qualified electronic signatures (QES)
A qualified electronic signature is an advanced electronic signature that is:
- created using a qualified electronic signature creation device such as USB tokens, smartcards, or remote creation devices
- based on a qualified digital certificate issued by a qualified trust service provider (QTSP)
In other words, a qualified electronic signature is an advanced e-signature that has reached a higher probative value by meeting these two additional requirements.
Under eIDAS, a qualified electronic signature has the same legal effect as a handwritten signature in all EU countries. Moreover, it is illegal for member states to request an electronic signature at a higher security level than the qualified electronic signature.
Are electronic signatures legal?
According to the EU’s eIDAS regulation, an electronic signature should not be denied legal effect and admissibility as evidence in court solely because it is in an electronic form. However, not all electronic signatures have the same legal effect.
- Simple electronic signatures: In most cases, simple electronic signatures won’t hold up if challenged in court.
- Advanced electronic signatures: Advanced electronic signatures have a higher probative value than simple electronic signatures. In most cases, advanced electronic signatures will hold up if challenged in court.
- Qualified electronic signatures: Qualified electronic signatures have the equivalent legal effect of handwritten signatures and will always hold up if challenged in court.
What is the difference between electronic signatures and digital signatures?
The term “electronic signatures” is commonly used to refer to simple electronic signatures. These e-signatures have the lowest security level and, therefore, can’t withstand scrutiny.
On the other hand, the term “digital signatures” is commonly used to refer to advanced and qualified electronic signatures. These e-signatures have a higher probative value than simple electronic signatures and, therefore, can be successfully used as evidence in legal proceedings.
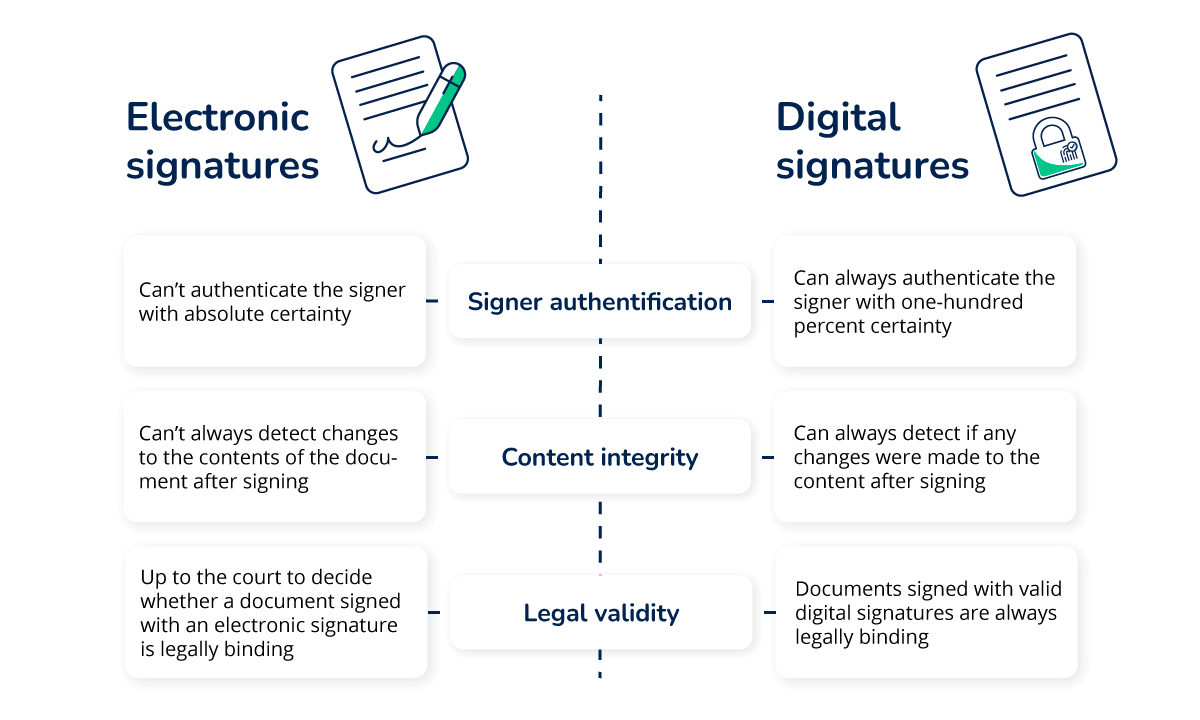
In conclusion, the difference between electronic signatures and digital signatures is that digital signatures have a higher level of security and greater probative value.
What are the benefits of using e-signature software?
Companies in various industries rely on e-signature software to reduce costs, boost the customer experience, and speed up signing processes. Here’s how e-signatures can help you optimize processes and provide a modern signing experience to your stakeholders.
- Workflow automation: When it comes to document signing, employees spend a lot of valuable time on manual tasks. E-signing software allows businesses to save time and reduce errors with the help of automation rules and automated reminders.
- Cost savings: Getting documents signed manually can be very expensive. By switching to e-signature software, companies can reduce the costs associated with manual work, paper, printing, and postage.
- Customer experience: E-signatures eliminate the hassle of printing and mailing documents. Customers can e-sign documents on their device of choice from anywhere and at any time. This improves convenience and boosts the customer experience.
Digital signatures provide additional benefits such as a high level of assurance, compliance with legal requirements, and increased security.
When can I use an e-signature?
Companies across multiple industries and departments use electronic signatures to overcome the challenges of paper-based processes and improve customer experience. Check out our Legality guide to find out what type of documents you can sign with an electronic signature in Belgium, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, and Finland.
Creating an e-signature with Penneo Sign
You can use Penneo Sign to create both simple electronic signatures and digital signatures.
You can create a simple electronic signature by:
- typing your name on the document
- drawing your signature with a mouse/touchpad
- inserting an image of the signature in the PDF
To create a digital signature with Penneo Sign, you need to use your national eID. Supported eIDs include itsme®, MitID, Swedish BankID, Norwegian BankID, Finnish Bank ID, and Mobiilivarmenne.
Start signing documents electronically with Penneo Sign
Are you in the market for secure e-signing software? Look no further than Penneo Sign.
Our solution helps you get rid of paper-based processes and automate manual work, so you can provide a modern experience to your clients and improve employee satisfaction.





