KYC, AML, and CDD are terms that are bound to come up when talking about anti-money laundering compliance. But what does each of these terms mean? And what is the main difference between them? Read on to find out.
What is KYC?
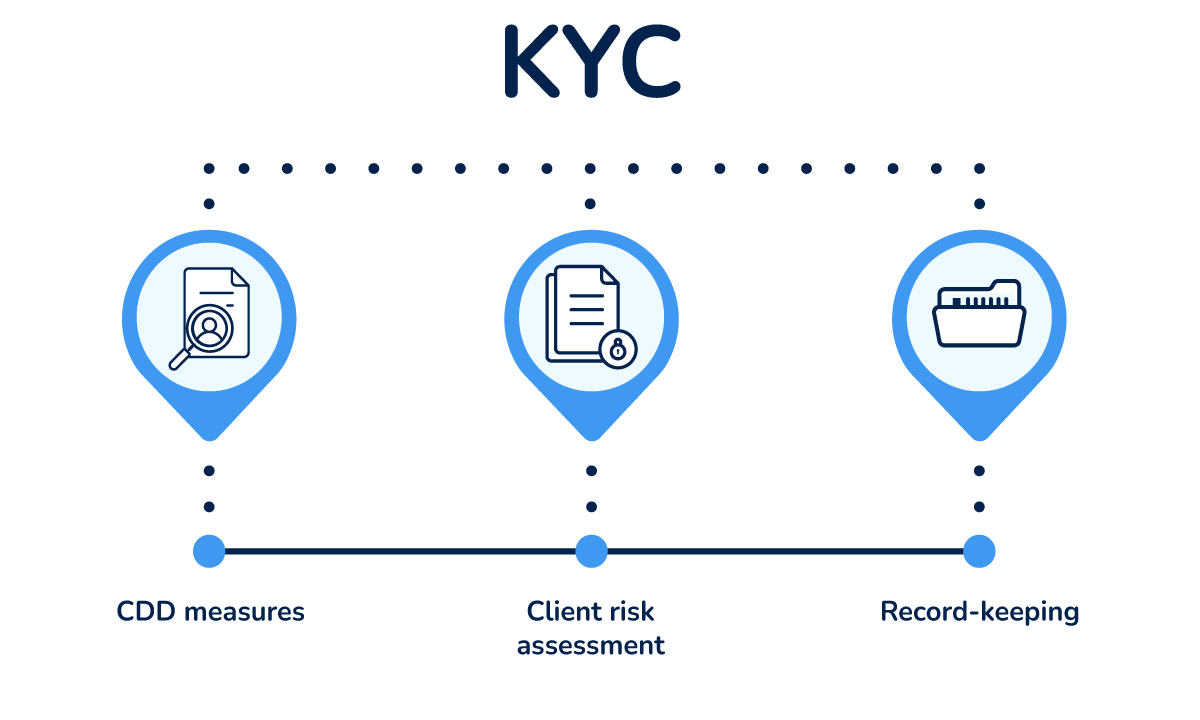
KYC or Know Your Customer is the process of verifying the identity of your customers, assessing their risk level, and continuously monitoring their activities and transactions. Carrying out a KYC process is a legal requirement for all businesses covered by anti-money laundering laws.
What is AML?
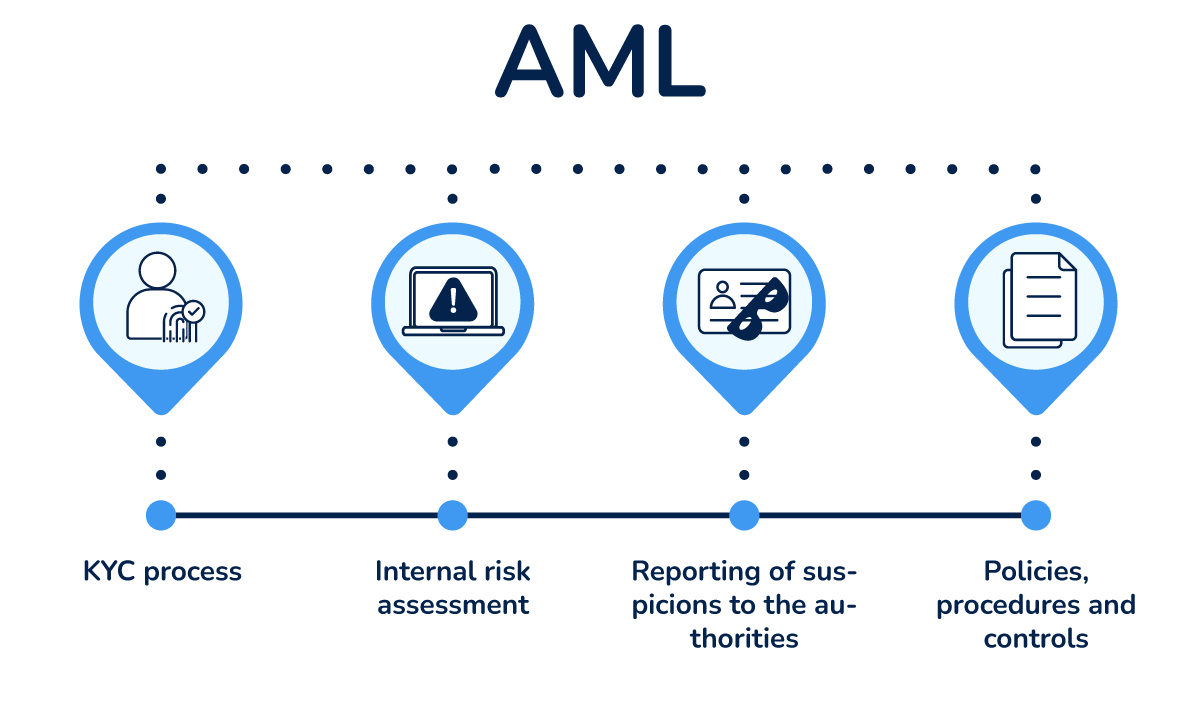
AML is short for Anti-Money Laundering and refers to all the obligations that companies covered by anti-money laundering laws must meet.
What is CDD?
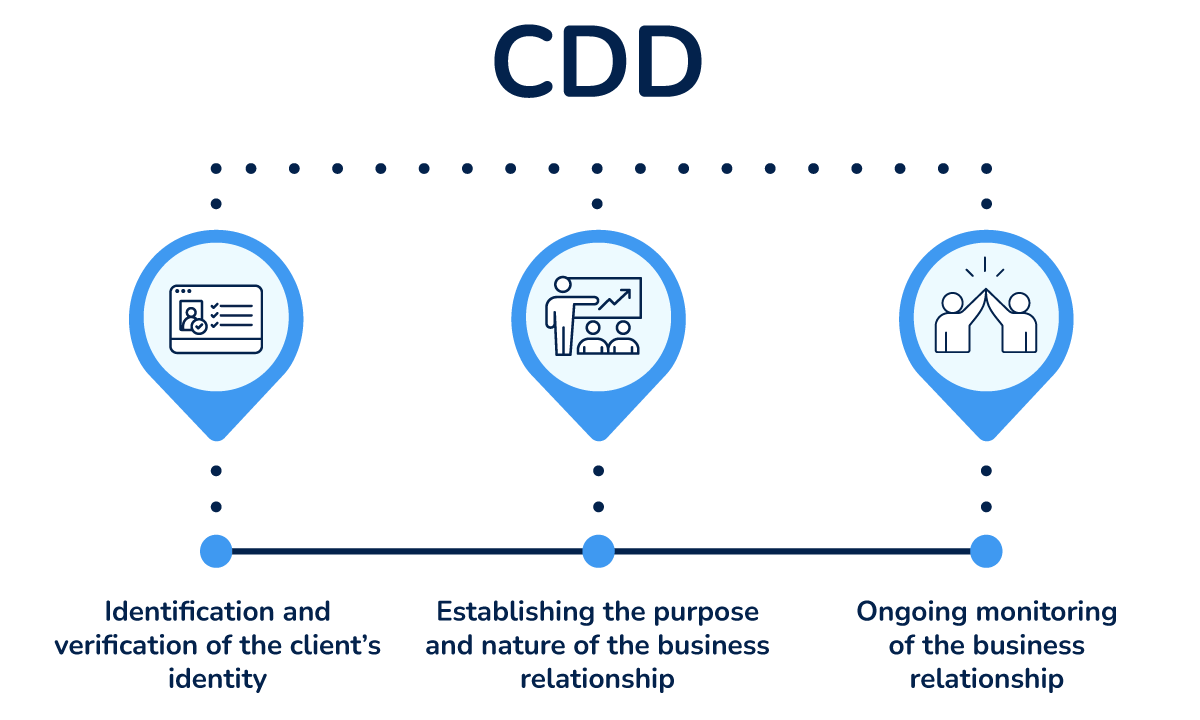
Customer due diligence (CDD) is a part of the KYC process. It refers to the measures taken to verify the identity of customers, establish the purpose and nature of business relationships, and continuously monitor client relationships.
What is the difference between KYC, AML, and CDD?
The difference between KYC and AML is that AML refers to all the anti-money laundering obligations that companies must meet, including the KYC process. Thus, KYC is only a part of an organization’s AML compliance program, alongside the internal risk assessment and the AML policies, procedures, and controls.
The difference between KYC and CDD is that customer due diligence (CDD) is only a component of the KYC process, alongside risk assessment and record-keeping.
| AML | KYC | CDD |
|---|---|---|
All the obligations that companies subject to anti-money laundering laws must meet, including:
|
A process that companies subject to anti-money laundering must carry out before establishing a new client relationship. The KYC process consists of the following:
|
A part of the KYC process comprising the measures taken to:
|
In conclusion, the KYC process is only one of the requirements for AML compliance, while CDD is only a part of the KYC process.
AML obligations in the EU
Since each EU country has its own anti-money laundering law, AML obligations often vary from country to country.
In this article, we’ll only list the AML obligations that all EU member states have in common:
1. Conducting a KYC process
The KYC process is an essential part of AML compliance. It helps businesses establish the identity of their customers and understand the money laundering risks associated with each client.
The main steps of a KYC process are:
Customer due diligence (CDD):
As part of CDD checks, you must collect the client’s identity information. In cases where a customer is a legal person, you must also obtain information about the customer’s beneficial owner(s).
Once you’ve gathered the necessary identity information, you must verify it. You can do this by requesting the client’s passport, national identity card, driver’s license, or another ID issued by a public authority.
After you have established that the client is who they say they are, you will need to determine the nature and purpose of the business relationship. Find out why the client wants to use your product or service and how they intend to use it (e.g., expected frequency and size of transactions).
Understanding the purpose and nature of the business relationship will help you assess the customer’s risk level and identify suspicious activities that don’t match the client’s expected transaction pattern.
Since a client’s circumstances can change, you must continuously monitor your customers throughout the business relationship. Moreover, you are legally required to promptly update any changes in the customer’s information and risk level.
All companies subject to AML laws must carry out customer due diligence. On top of that — in cases where a client poses a high ML/TF risk — the law requires enhanced due diligence (EDD) to be carried out.
Customer risk assessment
Another crucial step in the KYC process is to identify the risk associated with each client.
To accurately assess a customer’s risk profile, you should consider factors such as the client’s industry, the purpose and the nature of the business relationship, the client’s ownership and control structure, etc. On top of that, you must look up the client and its beneficial owner(s) on sanctions lists and PEP databases.
Record keeping
The record-keeping requirement differs from country to country.
In Denmark, Sweden, Norway, and Finland, companies must keep KYC records for five years from the end of the business relationship or occasional transaction.
In Belgium, KYC records must be kept for ten years from the end of the business relationship or occasional transaction.
2. Carrying out an internal risk assessment
The internal risk assessment helps obliged entities understand the money laundering risks relevant to their business and implement adequate policies, procedures, and controls to mitigate them.
When carrying out an internal risk assessment, you should consider the following factors:
- the type of products/services that you provide
- the types of clients that your business serves
- the geographical location of your clients
- the geographical location of your business
- your delivery channels and payment processes
3. Implementing policies, procedures, and controls
Companies subject to AML laws must implement policies, procedures, and controls to reduce the money laundering risks identified during the risk assessment.
4. Reporting suspicions of money laundering to the authorities
All businesses covered by AML laws must report suspicious activities and transactions to the relevant national authorities.
Digital tools for KYC/AML compliance
In the past few years, a number of RegTech solutions that can help simplify KYC/AML compliance have emerged.
Penneo KYC is one of the digital tools that can help you collect identity information from your customers, carry out a guided risk assessment, and continuously monitor your clients. Besides helping you make your KYC processes more efficient, Penneo KYC protects your clients’ information and documents via end-to-end encryption.
The solution boosts numerous features to help you save time, reduce costs, and provide a better onboarding experience to your clients.





