As a Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP), Penneo is authorized to offer qualified electronic signatures (QES). Qualified electronic signatures are the most secure type of digital signatures and have the same legal effect as handwritten signatures.
But what is a qualified electronic signature, exactly? And how is it different from an advanced e-signature?
What are the 3 types of e-signatures?
While all types of electronic signatures can be used to sign documents online, not all of them have the same probative value. An electronic signature’s probative value varies based on the level of security it provides.
In the European Union, the eIDAS Regulation defines the following three types of electronic signatures:
- Simple/Standard electronic signatures (SES)
- Advanced electronic signatures (AES)
- Qualified electronic signatures (QES)
| Signature type | Signer authentication | Content integrity | Non-repudiation | Based on a qualified certificate issued by a QTSP | Created by a qualified electronic signature creation device | Legal effect | Based on ETSI Standards | Sealed under PAdES Standard (by Penneo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard electronic signatures (SES) | No | No | No | No | No | Yes, but only in some cases | No | Yes |
| Advanced electronic signatures (AES) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes, in most cases | Yes | Yes |
| Qualified electronic signatures (QES) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes, in all cases | Yes | Yes |
What is a qualified electronic signature (QES)?
According to eIDAS, a qualified electronic signature is an advanced electronic signature that is:
- generated by a qualified signature creation device and;
- based on a qualified certificate for electronic signatures issued by a qualified trust service provider.
Due to the high level of security they provide, qualified e-signatures have the same legal effect as handwritten signatures.
What is a qualified certificate?
A qualified certificate is a digital certificate issued by a qualified trust service provider (QTSP) that contains the following:
- ❶ an indication that it is a qualified certificate for electronic signature;
- ❷ an indication of the qualified trust service provider issuing the certificate and the Member state where the QTSP is established;
- ❸ the name of the signatory, or a pseudonym;
- ❹ electronic signature validation data that corresponds to the electronic signature creation data;
- ❺ details of the beginning and end of the certificate’s period of validity;
- ❻ the certificate identity code, which must be unique for the qualified trust service provider;
- ❼ the advanced e-signatures or e-seal of the issuing qualified trust service provider and location.
| Qualified certificate for electronic signature ❶ | |
|---|---|
| Subject name ❸ | John Doe |
| Certificate serial number ❻ | 01946783 |
| Public key info ❹ | |
|
RSA |
|
013N5S8L40FKS |
|
2048 |
|
65437 |
|
EE:GE:69:7A:32:A l:D6:4E:F8:Q2… |
| Validity period ❺ | 2 years |
|
26/12/2021 |
|
25/12/2023 |
| Issuer Name ❷ | |
|
US |
|
Let’s encrypt |
|
FH02NT83625BF |
|
RSA |
| Certificate Authority’s digital signature ❼ | 10904J871N7903MH82G43KO… |
What is a qualified electronic signature creation device (QESCD)?
A qualified electronic signature creation device (QESCD) is the hardware or software used to create qualified electronic signatures. A signature creation device is “qualified” when it meets the requirements laid down in the eIDAS Regulation, and it’s managed by a Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP) such as Penneo.
Using a qualified electronic signature creation device better protects the digital certificates – mitigating any risk of replication or forgery. It also provides higher legal certainty for the qualified e-signature created with it.
A creation device can be a material object (like a smartcard or a USB token) in the signer’s possession and used together with a PIN code to sign. Think of a one-time code viewer used to access online banking services, for example.
The creation device can also be an electronic, immaterial object that is not necessarily in the physical possession of the signer but can be remotely managed by a qualified trust service provider. Such immaterial creation devices, known as remote qualified e-signature creation devices, improve the user experience while maintaining high legal certainty on the qualified e-signatures created with them.
At Penneo, we use physical qualified electronic signature creation devices which are securely stored and can be interacted with remotely through our servers. These devices, in combination with qualified digital certificates, allow us to create qualified electronic signatures.
How to create a qualified electronic signature
To create a qualified electronic signature, the signer must use an eID based on a qualified digital certificate.
The signer then proceeds to the authentication following the steps of the corresponding eID chosen – usually using their national identification number and passcodes or biometric identification.
At this point, the digital signing software takes over in enabling the creation of a qualified electronic signature through a series of steps:
- The software uses a qualified electronic signature creation device to interact with the signer’s private key
- The signer’s private key is used to sign the document
- The signing software (QTSP) acts as a Certificate Authority (CA) and issues a qualified electronic signature certificate
The software attaches the newly created signature, the signer’s digital certificate (eID), and the qualified electronic signature certificate to the document (via PKI). They become part of the signed PDF and cannot be separated from it.
As a final step, Penneo adds its own qualified seal to the document.
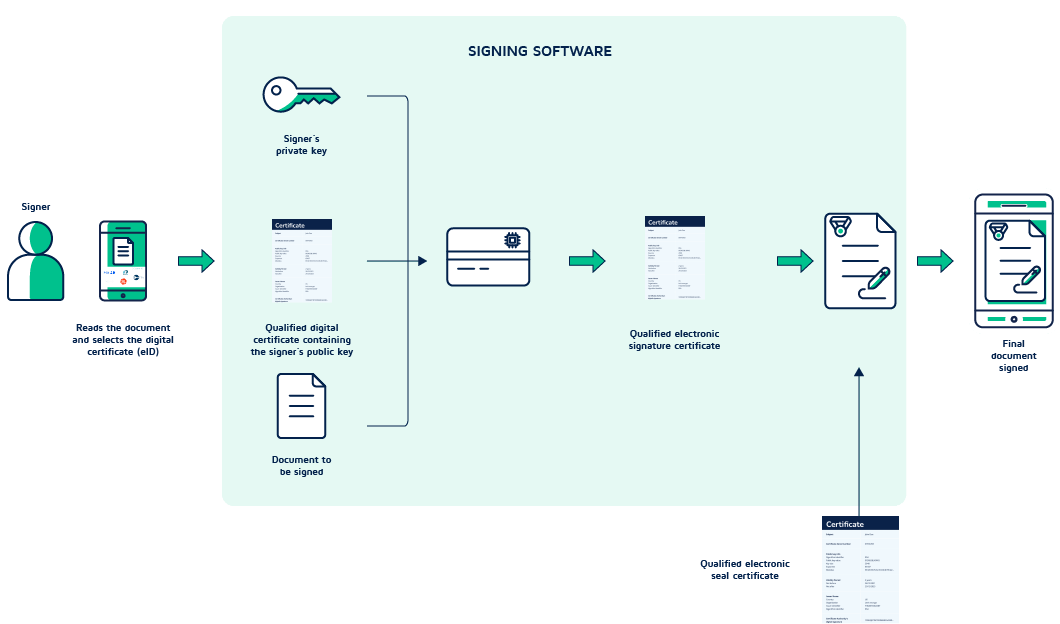
The signed document is then finalized and ready to be stored, downloaded, and distributed electronically.
How can you tell that a document has been signed with a qualified electronic signature?
When looking at the signed PDF, you won’t normally see any reference to the type of e-signature used to sign it. In other words, the signing software does not usually add any details on whether that e-signature is simple, advanced, or qualified.
Although that information is not visible on the document itself, it can still be found when opening it on a PDF reader or through a validator (like Penneo’s or the EU Commission’s validators).
Read more on how to verify the validity of a digital signature.
Create qualified electronic signatures via Penneo
Qualified electronic signatures are legally binding and court-admissible in nearly all possible cases where a document needs to be signed.
Penneo has been granted the status of Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP). Thus, in addition to advanced e-signatures, we have been authorized to provide qualified electronic signatures – the most secure type of e-signatures, which carry the highest probative value.
The type of signature you can create (qualified or advanced) will differ based on the Level of Assurance of your electronic ID.
Nonetheless, our strict compliance requirements as a QTSP consistently ensure an extra layer of security to your document transactions.





