All businesses that are subject to anti-money laundering laws must conduct a business-wide AML risk assessment to identify and assess the inherent ML/TF risks that they are exposed to. Understanding the risks of money laundering and terrorist financing that they are prone to enables companies to apply appropriate measures to mitigate these risks.
Obliged entities should use relevant documents such as national and supranational risk assessments as a starting point for their AML risk assessment. The risk assessment should be appropriate to the size and nature of their business. Obliged entities must review and update their risk assessment periodically or when circumstances change to ensure that the mitigating measures remain relevant and that any emerging ML/FT risks are promptly identified and addressed.
The risk assessment must be documented and made available to the relevant authorities upon request.
This article highlights the main risk factors that companies must take into account when conducting a business-wide AML risk assessment.
What are the ML/TF risk factors that companies must consider when conducting an AML risk assessment?
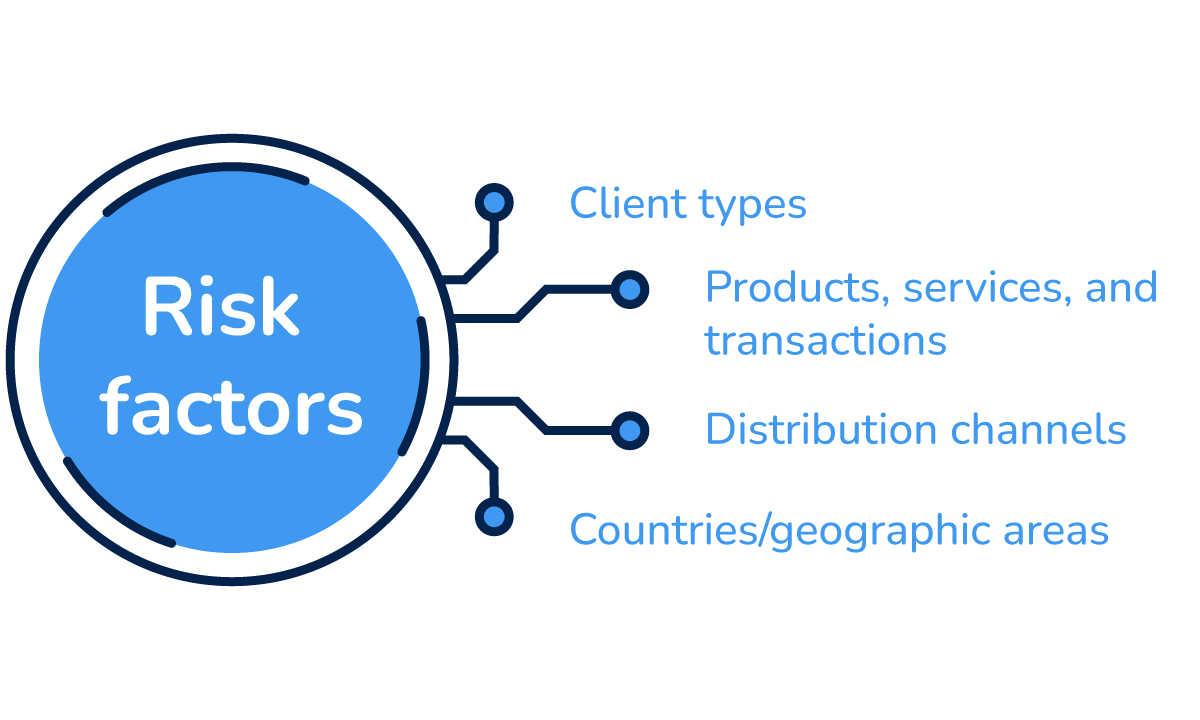
There are various risk factors that can impact obliged entities and increase the likelihood of them being used for money laundering or terrorist financing. Some of the most significant risk factors include:
- Client types
- Products, services, and transactions
- Delivery channels
- Countries/Geographic areas
Client types
The client types that the obliged entity serves must be taken into account during a business-wide AML risk assessment. Obliged entities must assess the risk of ML/TF that the different client types pose based on:
- The jurisdiction in which the clients and their beneficial owners are based
- The products and services that the clients provide
- The laws and regulations that the clients are subject to
- The clients’ ownership structures
- The clients’ reputations
Examples of client types that are usually associated with a potentially lower risk of money laundering and terrorist financing include:
- Clients that are listed companies and must comply with the disclosure requirements consistent with EU law
- Clients that are publicly owned enterprises or public administrations
On the other hand, the following client types are generally associated with a higher risk of ML/TF:
- Clients that are cash-intensive business, such as casinos, restaurants, pawn shops, bars, clubs, pubs, etc.
- Clients that provide products and services linked to a high-risk of ML/TF, such as money remittance services, currency exchange services, high-value goods, etc.
- Clients that are established or have business links in high-risk third countries
- Clients that have excessively complex or opaque ownership structures designed to conceal ultimate beneficial owner(s)
- Clients that seek anonymity and excessive secrecy
- Clients whose beneficial owners are politically exposed persons (PEPs) or close associates/relatives of PEPs
Products, services, and transactions
The products and services that it offers and the types of transactions that it carries out on behalf of customers can put the obliged entity at a heightened risk of being abused for money laundering and/or terrorist financing purposes.
When assessing the ML/TF risks associated with products, services, and transactions, companies should consider the following:
- The complexity of the products, services, and/or transactions
- The degree to which the products, services, and/or transactions allow for anonymity
- The size and value of transactions, services, and/or products
Examples of products, services, and transactions that usually carry a higher risk of ML/TF include:
- Trade finance
- Complex products, such as corporate banking
- Services that are capable of obscuring beneficial ownership from the authorities
- Transactions involving virtual assets for no apparent legitimate reason
- International correspondent banking services
- Money remittance and currency exchange
- Services where the obliged entity may in practice represent or assure the client’s standing, reputation and credibility to third parties, without a commensurate knowledge of the client’s affairs
- Services that rely heavily on emerging technologies
- Products and services that favour anonymity, such as electronic banking services
Conversely, the following products, services, and transactions are generally associated with a lower ML/TF risk:
- Life insurance policies where the premiums are low
- Workplace pension schemes where contributions are deducted directly from the wages
- Transactions that are carried out through an account in the customer’s name at a bank that is subject to AML laws
Distribution channels
The most significant ML/TF risks associated with distribution channels are the use of intermediaries (agents) and non-face-to-face business relationships without the use of adequate safeguards (e.g., eIDAS-compliant electronic identification).
Countries/geographic areas
The countries in which it operates can influence the money laundering and/or terrorist financing risks that an obliged entity is exposed to.
Obliged entities that are established or operate in any of the countries that appear on the EU Commission’s list of high-risk third countries are at a higher risk for ML/TF. This is because the countries featured on the EU Commission’s list have significant deficiencies in their AML/CFT regimes.
On the other hand, obliged entities that are established or/and operate in countries that have an AML/CFT regime that is not less robust than that required by the EUs AML Directive, carry a potentially lower risk of ML/TF.
What are the next steps?
Once the company has identified the ML/TF risks, and determined each risk’s likelihood and potential impact, they must implement mitigation measures that are commensurate with the risks. This risk-based approach ensures that companies focus their efforts and allocate resources to effectively address the most significant risks.
How can Penneo KYC assist you with the AML risk assessment process?
Penneo KYC is a digital solution that enables companies to meet their AML/KYC obligations in an efficient, secure, and compliant manner.
Notable features of Penneo KYC include:
- Digital verification of the clients’ identities
- End-to-end encrypted data collection
- Guided risk assessment
- Unlimited KYC verifications
- Automated company and UBO data retrieval from UBO registers and official company databases
- Automated PEP identification
- Daily screening of clients and UBOs against sanctions lists
- Activity log to demonstrate your compliance to the authorities
- Instant notifications regarding changes in your clients’ circumstances
With Penneo KYC, complying with AML laws doesn’t have to be a burden.





