Electronic seals are used to ensure the origin and integrity of electronic documents issued by legal entities. By using electronic seals, businesses can protect themselves and their stakeholders against fraud.
What are electronic seals?
The eIDAS regulation defines electronic seals as data in electronic form, which is attached to or logically associated with other data in electronic form to ensure the latter’s origin and integrity.
Businesses can use electronic seals to prove that they are the issuers of an electronic document and that the document has not been tampered with. Electronic seals can be applied to all types of electronic documents – from employment contracts and tax declarations to invoices and non-disclosure agreements.
Legal entities must employ the services of a Trust Service Provider for electronic seals to electronically seal their documents in a secure and compliant manner.
Types of electronic seals
Based on their level of security, the EU’s eIDAS regulation defines three types of electronic seals:
- Simple electronic seals
- Advanced electronic seals
- Qualified electronic seals
1. Simple electronic seals
As mentioned above, a simple electronic seal is any data in electronic form, which is attached to or logically associated with other data in electronic form to ensure the latter’s origin and integrity.
2. Advanced electronic seals (AdESeal)
An advanced electronic seal is a type of electronic seal that meets the following security requirements set out by the eIDAS regulation:
- It is uniquely linked to the legal entity that created the seal;
- It is capable of identifying the legal entity that created the seal;
- It is created using electronic seal creation data that is under the sole control of the legal entity that created the seal, and
- It is linked to the data to which it relates in such a way that any subsequent change in the data is detectable.
Similar to advanced electronic signatures, advanced electronic seals are also based on PKI technology and digital certificates issued by recognized Trust Service Providers.
According to the eIDAS regulation, an advanced electronic seal is admissible as evidence in legal proceedings.
3. Qualified electronic seals (QESeal)
A qualified electronic seal is an advanced electronic seal which is additionally:
- Created using a qualified seal creation device (QSCD), which provides high assurance of the security of the seal
- Based on a qualified certificate for electronic seals issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider, which provides high assurance of the identity of the creator of the seal
In other words, a qualified electronic seal is an advanced electronic seal that provides a stronger specific legal effect and higher security by meeting these two additional requirements.
How are qualified electronic seals created?
Qualified electronic seals use PKI technology and qualified electronic certificates to ensure the origin and integrity of the sealed document. Let’s see how that works in practice.
- 1. The creator of the seal uploads a PDF document to the application.
- 2. The application generates a hash value of the document at the time of sealing and presents it to the qualified seal creation device.
- 3. The seal creation device will ask the creator of the seal to authenticate themselves.
- 4. Once the creator has completed the authentication process, the qualified seal creation device creates the seal, and the application integrates the seal into the document.
- 5. The qualified electronic certificate is also provided with the sealed data to enable the identification of the seal creator and the verification of the seal.
What is the difference between electronic signatures and electronic seals?
The difference between electronic signatures and electronic seals is two-fold:
Electronic signatures can only be created by natural persons (private individuals) and are used to bind a signer to the content of the signed document. On the other hand, electronic seals can only be created by legal entities and are used to guarantee and verify the origin and integrity of electronic documents.
What are the benefits associated with electronic seals?
Many companies are using electronic seals to enhance the security and legal certainty of their electronic transactions. Let’s take a closer look at the main benefits associated with electronic seals.
Certainty about the origin of the document: Electronic seals are based on electronic certificates issued by Trust Service Providers. These certificates serve as evidence that an electronic document was issued by a legal entity that created the seal.
Certainty about the integrity of the document: Providers of advanced and qualified electronic seals use PKI technology to ensure that the sealed document hasn’t been tampered with.
Legal effect: The eIDAS regulation stipulates that electronic seals should not be denied legal effect simply because they are in electronic form. Therefore, businesses can use electronic seals as evidence in legal proceedings.
Higher efficiency: Businesses can use digital tools to automate the electronic sealing of documents, thus improving efficiency and productivity.
Qualified electronic seals also provide additional benefits such as EU-wide recognition and interoperability.
How can I see the document seal and check its validity
When you open a signed PDF in Adobe Reader, the first thing you see is the seal of the document. In Adobe Reader, the seal appears as a blue bar at the top.
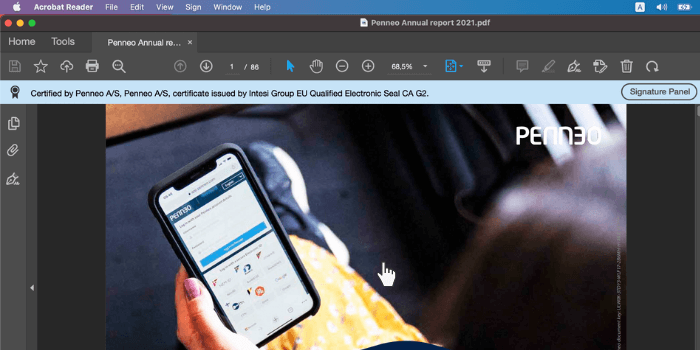
For documents signed via Penneo, the seal is a qualified electronic seal issued by Intesi Group, an EU Qualified Trust Service Provider certified under eIDAS standards.
The seal guarantees the probative value of the document. If the document is not legally valid, the bar will show the following text: Certification by Penneo A/S is invalid
.
The qualified electronic seal is applied by Penneo at the end of the signing process. After the signers have signed the document, Penneo seals the signed document according to the PAdES standard.
By applying the final seal to the document, it’s as if Penneo acted as the last and final signer of the document. The seal is incorporated directly within the signed PDF – as much as an ink signature becomes an integral part of a paper document – and as such it guarantees the full signed document, including both its content and its signers’ signatures.
This ensures that the document never loses its legal reliability, as the complete self-contained PDF file contains everything you need to verify the signatures’ validity and remain valid for long periods. At the same time, the PDF file can be copied, stored, and distributed as a simple electronic file.
Conclusion
Electronic seals – especially qualified electronic seals – enable companies, organizations, and government institutions to carry out electronic transactions and provide online services in a more secure and reliable manner. This, in turn, helps them build and preserve the trust of their customers and stakeholders.